Gradle素人なので、GradleのホームページにあったサンプルをKotlinで動かしてみた。
[マルチプロジェクトのプロジェクト作成]
gradle initで対話型でプロジェクトを作成する。サンプルではJavaを選択しているが、今回はKotlinを選択してみた。
$ gradle init Starting a Gradle Daemon (subsequent builds will be faster) Select type of project to generate: 1: basic 2: application 3: library 4: Gradle plugin Enter selection (default: basic) [1..4] 2 Select implementation language: 1: C++ 2: Groovy 3: Java 4: Kotlin 5: Scala 6: Swift Enter selection (default: Java) [1..6] 4 Split functionality across multiple subprojects?: 1: no - only one application project 2: yes - application and library projects Enter selection (default: no - only one application project) [1..2] 2 Select build script DSL: 1: Groovy 2: Kotlin Enter selection (default: Kotlin) [1..2] 2 Project name (default: multi-project-sample): Source package (default: multi.project.sample): > Task :init Get more help with your project: https://docs.gradle.org/7.0.2/samples/sample_building_kotlin_applications_multi_project.html BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 59s 2 actionable tasks: 2 executed
以下の質問で2を選択すると、それだけでマルチプロジェクトな構成になる。
Split functionality across multiple subprojects?: 1: no - only one application project 2: yes - application and library projects Enter selection (default: no - only one application project) [1..2]
作成されたプロジェクトは以下のようになる。
$ tree -L 2
.
├── app
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ └── src
├── buildSrc
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ └── src
├── gradle
│ └── wrapper
├── gradlew
├── gradlew.bat
├── list
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ └── src
├── settings.gradle.kts
└── utilities
├── build.gradle.kts
└── src
ディレクトリ直下にbuild.gradle.ktsがない。どうなっているんだろう?
settings.gradle.ktsを見ると、3つのサブプロジェクトがあることが分かる。
rootProject.name = "multi-project-sample"
include("app", "list", "utilities")
[ビルドロジックの集約]
各プロジェクトのビルドロジックや設定はbuildSrcディレクトリに集約されている。
共通のビルドロジックがこのファイル。
buildSrc/src/main/kotlin/multi.project.sample.kotlin-common-conventions.gradle.kts
/*
* This file was generated by the Gradle 'init' task.
*/
plugins {
// Apply the org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm Plugin to add support for Kotlin.
id("org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm")
}
repositories {
// Use Maven Central for resolving dependencies.
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
constraints {
// Define dependency versions as constraints
implementation("org.apache.commons:commons-text:1.9")
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk8")
}
// Align versions of all Kotlin components
implementation(platform("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-bom"))
// Use the Kotlin JDK 8 standard library.
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk8")
// Align versions of all Kotlin components
implementation(platform("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-bom"))
// Use JUnit Jupiter API for testing.
testImplementation("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.7.1")
// Use JUnit Jupiter Engine for testing.
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine")
}
tasks.test {
// Use junit platform for unit tests.
useJUnitPlatform()
}
これを利用したプロジェクトごとのビルドロジック。
buildSrc/src/main/kotlin/multi.project.sample.kotlin-library-conventions.gradle.kts
/*
* This file was generated by the Gradle 'init' task.
*/
plugins {
// Apply the common convention plugin for shared build configuration between library and application projects.
id("multi.project.sample.kotlin-common-conventions")// 先ほどの共通規約を適用
// Apply the java-library plugin for API and implementation separation.
`java-library` // APIと実装の分離のためのプラグイン
}
buildSrc/src/main/kotlin/multi.project.sample.kotlin-application-conventions.gradle.kts
/*
* This file was generated by the Gradle 'init' task.
*/
plugins {
// Apply the common convention plugin for shared build configuration between library and application projects.
id("multi.project.sample.kotlin-common-conventions")// 先ほどの共通規約を適用
// Apply the application plugin to add support for building a CLI application in Java.
application // CLIアプリケーションプラグイン
}
これらの設定を、各プロジェクトのbuild.gradle.ktsファイルでプラグインとして指定する。
app/build.gradle.ktsファイルの中身はこうなっている。
plugins {
id("demo.java-application-conventions") // ここでbuildSrcで定義した規約を指定する
}
dependencies {
implementation("org.apache.commons:commons-text")
implementation(project(":utilities"))
}
application {
mainClass.set("demo.app.App")
}
ライブラリ側も同様。
list/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
id("demo.java-library-conventions")// ここでbuildSrcで定義した規約を指定
}
utilities/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
id("demo.java-library-conventions")// ここでbuildSrcで定義した規約を指定
}
dependencies {
api(project(":list"))
}
ビルド関連のファイルとしては最後にbuildSrc/build.gradle.ktsがある。サンプルで説明されているJavaの場合と違って、dependenciesが追加されている。利用言語にKotlinを選択したためのようだ(Javaを選択した場合にはdependenciesブロックはなかった)。
plugins {
// Support convention plugins written in Kotlin. Convention plugins are build scripts in 'src/main' that automatically become available as plugins in the main build.
`kotlin-dsl` // src/main以下のスクリプトがプラグインとして利用可能になる
}
repositories {
// Use the plugin portal to apply community plugins in convention plugins.
gradlePluginPortal()
}
dependencies {
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin")
}
[その他便利コマンド]
プロジェクト直下で利用可能なコマンドとしては他に以下のものがある。
- テスト実行:./gradlew check
- アプリケーションを実行:./gradlew run
- パッケージング:./gradlew build
パッケージングコマンドを実行すると、app/build/distributions/app.tar と app/build/distributions/app.zipを生成してくれる。
また、ビルドの詳細を見ることができるスキャンオプションも利用できる。先日ブログのコメントでTODA先生に教えていただいたやつ。
$ ./gradlew build --scan BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 29s 16 actionable tasks: 8 executed, 8 up-to-date Publishing a build scan to scans.gradle.com requires accepting the Gradle Terms of Service defined at https://gradle.com/terms-of-service. Do you accept these terms? [yes, no] yes Gradle Terms of Service accepted. Publishing build scan... https://gradle.com/s/XXXXXXXXXXXXX
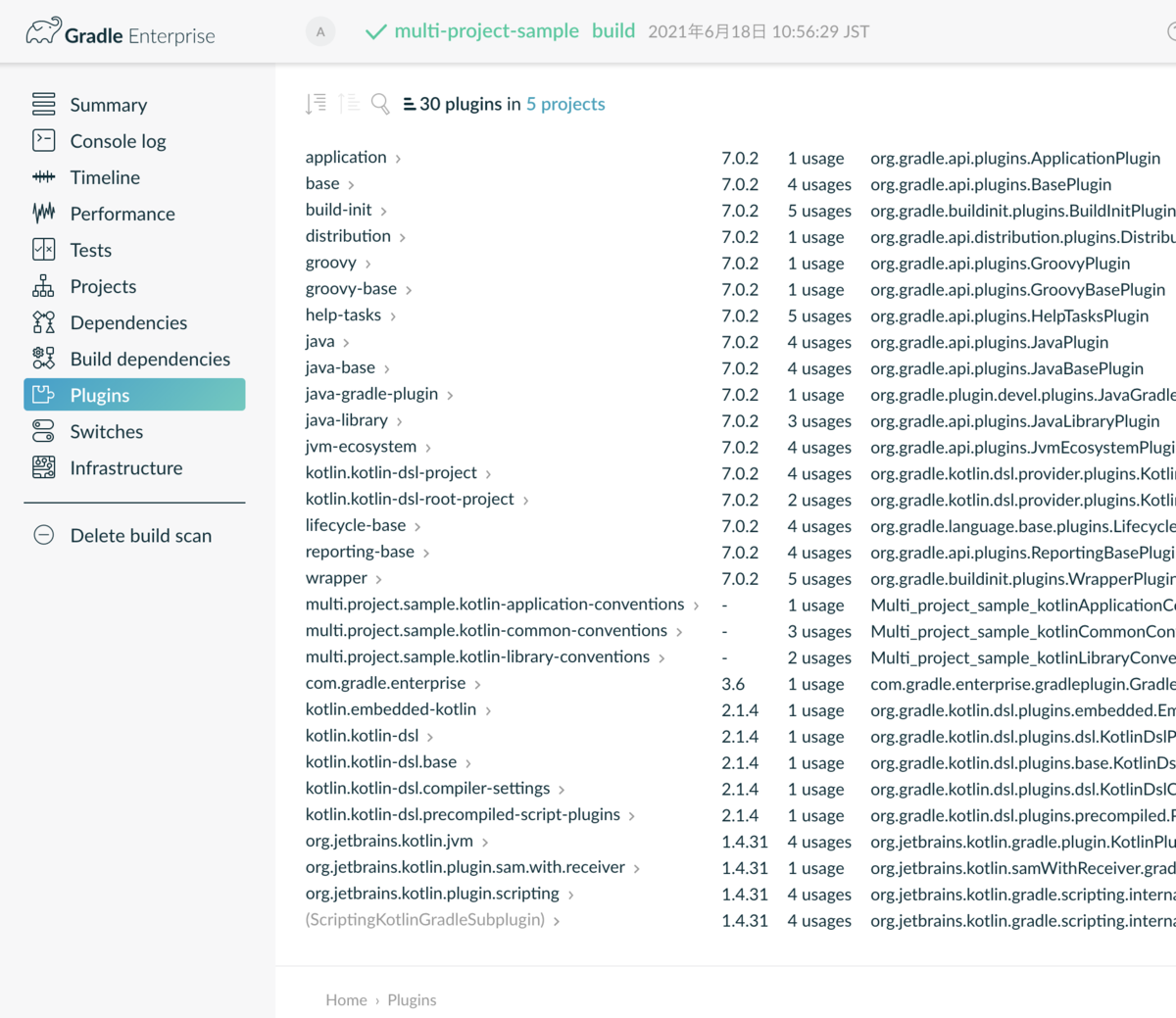
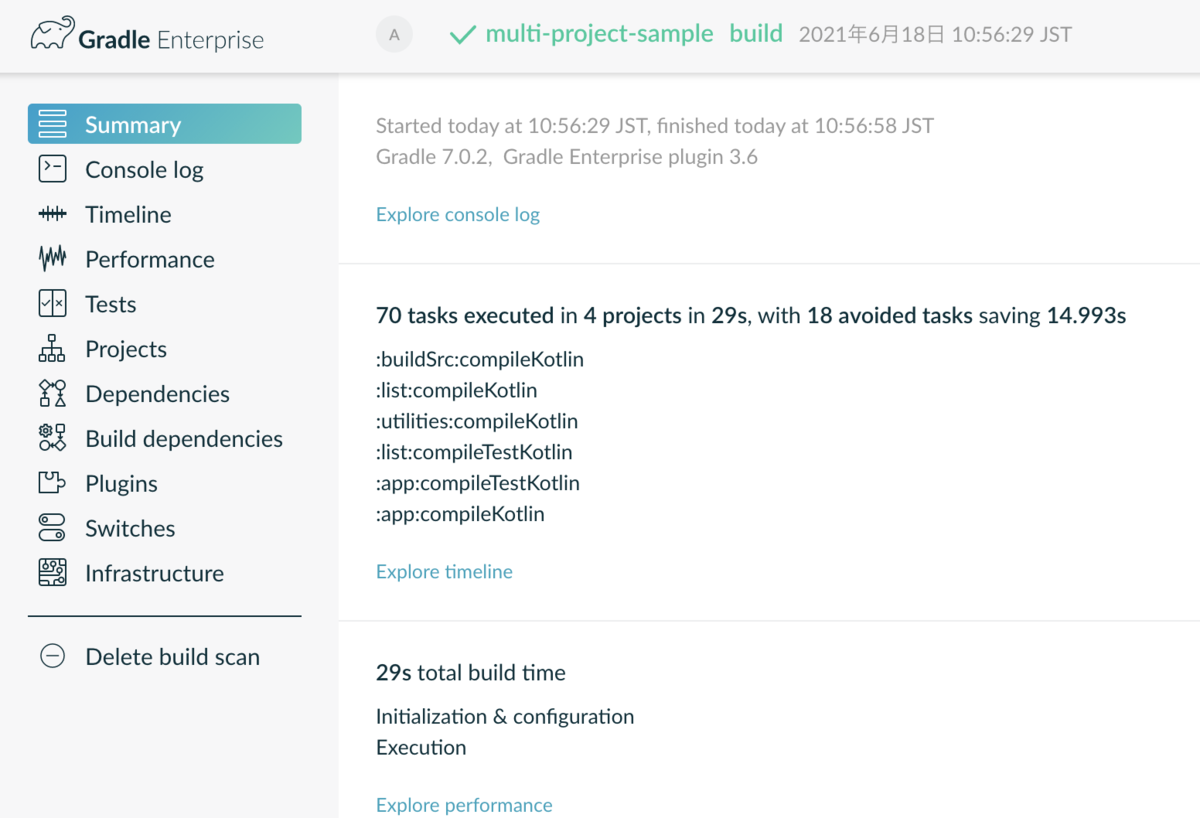
最後に表示されたURL開くと以下のような画面が表示される(初回のみメールアドレスの設定が必要)。
ビルド時にどのようなGradleプラグインが利用されているかも分かる。こんなにいっぱいプラグインが動いているのか……それぞれ何してるのか全くわからないので、今度調べてみよう。